Day :
- Food Safety,Nutrition and metabolism,Clinical Nutrition,Public Health Research,Food Processing Technology

Chair
Ozlem Tokusoglu
Session Introduction
Giorgio Rusconi
Mondini Rusconi Law Firm
Title: Food Technology: Innovation before Legislation or Legislation before Innovation?â€

Biography:
Having worked as a food lawyer since the industry’s infancy, Giorgio Rusconi has significant experience in food law, assisting Italian and foreign clients with hygiene, labelling, additives, organic farming, geographical indications/destinations of origin, packaging, and responsibilities regarding food products and within the industry. Rusconi also defends clients in civil and criminal litigation, centering on product liability. He is the 2017 TopLegal Food Lawyer of the Year, ranked on The Legal 500’s elite ‘Leading Lawyers” list for Food, and helped establish FLN - Food Lawyers’ Network Worldwide, offering integrated legal services to food industry multinationals in 50 countries
Abstract:
Mechanically separated meat (MSM)—which must be ret ailed in some kind of cooked form because of the risk of microbial contamination, in contrast to the higher price-fetching minced meat—makes it possible for producers to realize add ed profits from offals, a market estimated to be between €400 million and €900 million in size. EU r egulations distinguish MSM from cut or minced meat, but the distinctions are not always clearly delineated, given the nature of reduced meat products (RMP). In the recent Newby case (C-453/13), the EU Court of Justice determined that an industry innovation did not, in fact, create a new meat product because the final product met the definition of MSM. The decision signals that innovations in the processing of MSM will not result in new designations that fall under RMP if within the innovation basic definitions of MSM are already met. This is true even if the innovation produces something that is visibly very different in appearance from traditional MSM.
The reported case on MSM is one of various examples that can be made in the ambit of the discussion about the topic “Food Technology: Innovation before Legislation or Legislation before Innovation?”. Of course, progress and innova tion are subsequent to R&D activities whilst new legislations are subsequent to public consultations, comitology and political debates. On this respect, is legislation far behind innovation? And how this gap can be narrowed?
Christine FEILLET-COUDRAY
Univ Montpellier, Montpellier, France
Title: Toxicity in Rats of a Betaine/Glycerol Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent (NADES) for Phenolic Compounds Extraction

Biography:
Christine FEILLET-COUDRAY graduated from Montpellier Biological and Food Engineering School in 1991 and obtained Ph.D. in 1995 at the Faculty of Medicine of Montpellier. She works at the National Institute of Agronomic Research. Her research interests range over both micronutrients and oxidative stress physiopathology, and more generally malnutrition and its relation to the development of metabolic syndrome components.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: NaDES (natural deep eutectic solvents) are new natural solvents in green chemistry and have been shown to allow better extraction of plant bioactive molecules, particularly phenolic compounds, by comparison to conventional solvent. NaDES would allow higher phenolic compounds absorption in mice following oral administration. However, there is a lack of information aregarding their in vivo safety. The purpose of this short study was to verify the safety in rats of a mixture of polyphenols extracted from green coffee beans with NaDES.
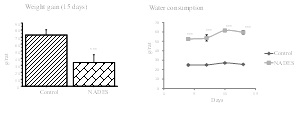
Materials & Methods: Green coffee phenolic compounds at 10 mg of chlorogenic acid equivalent/mL were extracted by NaDES betaine:glycerol (mole ratio 1:2) + 10 water (v/v). Twelve 6-weeks-old male Wistar rats were randomized into two groups of 6 animals and gavaged for 14 days either with water or with phenolic NaDES extract. Rat body weight, food consumption and drinking were determined every two days. Rats were then sacrificed and blood and tissues collected. Plasma/serum routine biochemical analyses were performed (glucose, creatinine, lipids, ASAT/ALAT, uric acid, and urea). Lipid (TBARS), protein (thiols and AOPP) and glucose oxidation (AGEs) products were measured in plasma and liver. Liver lipid and glycogen content were also quantified. Findings: oral administration of phenolic NaDES extract induced mortality in 2 mouse. In addition, it induced excessive water consumption, reduced dietary intake and weight loss, hepatomegaly, plasma oxidative stress associated with high blood lipid levels. Conclusion & Significance: this work demonstrated the toxicity of oral administration of the NaDES: betaine/glycerol, under the acute conditions tested. This occurs despite the fact that this NaDES extract contains polyphenols, the beneficial effects of which have been shown to be numerous. Therefore, complementary work is needed to find the best dose and formulation of NaDES that are safe for the environment, animals and ultimately for humans.
Figure 1: Rats weight gain at the end of the study and water consumption along the study
Raushan Tuleuova
West Kazakhstan Marat Ospanov State Medical University, Kazakhstan
Title: Validation of a Kazakh Food frequency questionnaire

Biography:
Raushan Tuleuova Master of Medicine, PhD candidate, works as teacher of preventive medicine. At the moment, providing an investigation in the field of epidemiology of nutrition of the Kazakh population, the influence of dietary habits on the development of cardiovascular diseases, prevention and reduction of the incidence of cardiovascular diseases.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Food frequency questionnaire is widely used, validated food study tool. There are a number of indicators that need to be optimized for the study population of the Russian and Kazakh variants of the questionnaire: food items, availability of food products, volume of portions, accounting of ingredients in the food, and food habits.
The aim of the study is to create FFQ_KZ, which accounts the products consumed in Kazakhstan, and its validation.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation. A survey of 60 representatives of the Kazakh population was conducted. The age (mean, SD) of subjects was 62.9±6.5 years. FFQ consisting of 117 items, translated into Russian and Kazakh by two independent translators from the format "The European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC) Norfolk FFQ", and test 24-hour recall were used. The correlation analysis of Spearman in Statistica-10 was performed to compare the results of two methods of evaluation of nutrition for energy value, macro - and micronutrients.
Findings: We replaced 4 products: "salted meat" on "horse meat", "beefburgers" on "cutlets, meatballs, stuffed cabbage, manty", "brown rice" replaced by "buckwheat, millet", in the item "savoury pies" added "pies with unsweetened fillings".
Statistically significant (p<0.05) high correlation coefficients were found for energy (0.92), proteins (0.9), total fat (0.86), saturated (0.8) and polyunsaturated (0.87) fats, cholesterol (0.87), iron (0.85), vitamin B1 (0.75), B2 (0.85). Average correlation was found for carbohydrates (0,59), vitamins C (0,58) and A (0,46); weak correlation – for calcium (0,32) and potassium (0,37). No statistically significant relationship between monounsaturated fats (0.03) and vitamin E (0.06) was found.
Conclusion & Significance. According to the main micro and macronutrients, the energy value modified FFQ_KZ is a valid tool for analyzing the nutrition of the Kazakh population
Harini N.B,
Nutritionist,Almond Board of California, India
Title: Association between flavonoid intake and risk of cardio-vascular disease among post-menopausal women

Biography:
Harini N B has completed her MSc and BSc Degrees in Clinical Nutrition from Sri Ramachandra University and Ethiraj College for Women, respectively. She is currently a Consultant Nutritionist at Almond board of California and delivers lectures on the importance of the nutritional values of almonds and its health benefits. She has worked at the Apollo hospitals, India as a Clinical Dietitian Associate for a year where she performed nutrition counseling, assessed the nutritional requirements and developed nutrition counseling programs for the patients and suggested diet charts to meet individual’s requirements. She was actively involved in organizing the Bariatric nutrition conference “Enlight 2016”.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Flavonoid intake has been proven to reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. Post-menopausal women are at a higher risk of getting heart disease because of altered hormone levels. Good nutrition counseling associated with strategies to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease can help subjects’ live longer, healthy life.
Aim: To study the association of cardiovascular disease risk with flavonoid intake, nutrient intake, BMI, lipid levels in post-menopausal women.
Materials & Methods: It was a prospective observational study which consisted of 100 post-menopausal subjects. Subjects were assessed of parameters like height, weight, BMI, total cholesterol, HDL, nutrient intake and flavonoid intake. They were also assessed using Framingham Risk Score sheet to find out the risk of developing heart disease in next ten years.
Results: Total cholesterol was highest and HDL was lowest in the high risk group which was found to be significant (p<0.001). The fat intake was observed to be 38.35±6.04 g, 46.67±10.19 g, 53.63±9.00 g in low, intermediate and high risk groups, respectively, which was also found to be highly significant (p<0.001). It is observed that intake of flavonoid was 306.07±14.92 g, 212.08±45.08 g and 229.65±64.01 g in low, intermediate and high risk category, respectively which was found to be highly significant (p<0.001). Negative correlation was found with flavonoids, HDL and the risk scores (p<0.001) which illustrates the proven fact that as flavonoid intake increases, risk for developing heart disease decreases.
Conclusion: High intake of flavonoids and low intake of fat seems to have less risk of cardiovascular disease, whereas value of high cholesterol and low HDL are considered as risk factors for developing CVD. It is mandatory for women beyond 40 years to be educated on lifestyle modification with more emphasis on reduction of fat and maintenance of appropriate body mass index and increased intake of flavonoids.
Aparajith Hettiarachchi
University of Moratuwa, Sri Lanka
Title: A model of food security management system for edible oil and oil based products used for cooking purposes

Biography:
Aparajith Manupriya Hettiarachchi is a quality assurance manager in Harumi Holdings (Pvt.) Ltd. (brand name: Dreamron profional cosmetics), in Sri Lanka, since April 2017 to up to date. Before joining to Harumi Holdings (Pvt.) Ltd., he was worked as a food auditor in SGS Lanka (Pvt.) Ltd., year 2015 to 2017. He is qualified lead auditor in food safety management system for the following food safety management system standards: ISO 22000:2005, FSSC 22000:2013, BRC, HACCP and GMP. Also, he is qualified lead auditor in quality management system ISO 9001:2015. In year 2010 to 2015, he was worked at Bio Extracts (Pvt.) Ltd., Expolanka Group as a quality assurance executive - Quality System Compliance and R & D.
He was obtained B. Sc in Molecular Microbiology, Kazan State University, Russia in 2006 and M.Sc. in Industrial Utilization of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants, University of Sri Jayawardanapura, Sri Lanka in 2012 and currently reading a MBA in Management of Technology, University of Moratuwa, Sri Lanka. Currently he is awaiting for the PhD in Food Science and Technology in University of Queensland, Australia.
He has done many researches including international publications in areas of medical microbiology, carcinogenicity of mushrooms and food security. His research interests are food
Abstract:
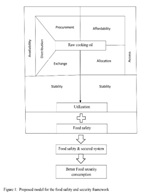
Food safety and food security are interrelated concepts with a profound impact on quality of human life. In 2009, the World Summit on Food Security introduced four pillars of food security namely; availability, access, utilization and stability. Food security could be substantially improved by increased investment and policy reforms. The ISO 22000:2005 family of international standards is one of leading food safety security management systems and it specifically addresses food safety management. However, the scope of food security is insufficiently addressed by the ISO 22000:2005 food safety standards. The purpose of this study is to develop an extended framework of standards opposed to ISO 22000:2005 food safety standards considering one additional pillar in food security, which is food safety, with a special reference to edible oil and oil based products in Sri Lanka. Among 745 Colombo Municipal Council (CMC) registered food preparation facilities, 75 facilities were selected as a stratified random sample. A self-administered online questionnaire was used to identify gaps in local food security practices in edible oil. Of the total responders, 60% were chefs and 40% were hotel managers. Out of total, 73% were eating houses and 11% were hotels. But only from the total sample 10% has been certified for system standards and 50% of it was certified with ISO 22000. About 55% food outlets used palm oil as the main cooking oil and cost, availability and popularity were the main reasons. Only 5% of the sample considered nutritional value and health impact in using cooking oil. However, 52% of the sample used cooking oil for frying despite of the awareness on adverse health consequences from frying with palm oil. The results of the survey revealed that the Sri Lankan food preparation facilities are significantly behind in food security practices because they match more considerable about food safety management principles. Therefore, in addition to food safety management system, we suggest to include four pillars in food security systems into the standard because of significantly food security practices are lacking in our current system.
Durgeshwori Munankarmi
Nutrition Society, UK
Title: Food and nutrient intake of recent immigrants in Sheffield

Biography:
Durgeshwori Munankarmi ANutr has completed her MMedSci Human Nutrition with merit from the University of Sheffield, United Kingdom in 2016. She has completed her Bachelors in Nursing and Proficiency Certificate Level in Nursing both with distinction from Institute of Medicine, Tribhuvan University, Nepal. She is an early Researcher with vivid interest in research related to health and nutrition and always shown remarkable outcome of her research reports. She has experience of conducting systematic review, observational studies, surveys and other qualitative research. She has presented her research in national and international scientific conference and has successfully published her paper in an open access journal. Currently, she is working as Freelancer Researcher
Abstract:
Background: Refugee and asylum seekers are not a new situation in UK, as there have always been episodes of migration to Britain. The movement of populations from developing countries and across Europe is increasingly a topic for health and nutrition research, yet scant attention has been paid to assessment of health and nutrition among the wide diversity of immigrant groups recently arriving in the UK.
Aim: The main aim of this study is to explore Sheffield refugees’ experience of food poverty and to assess the level of adequacy of their diet.
Methods: In this cross sectional survey, 50 refugee or asylum seekers accessing two charitable services in Sheffield, UK were interviewed. A semi structured questionnaire was used to gather data about demography, health and life style, eating habit, multiple pass 24 hour recall was used to find out the food intake.
Results: Total energy intake for all age group and each sex was significantly lower than the estimated average requirement in study population. Intake of all micronutrient was below the reference nutrient intake. Consumption of fruit and vegetable was very low. Financial constraint was the most common cause of not having balanced diet.
Conclusion: This study reveals the risk of dietary inadequacy in refugee and asylum seekers. This study group is in risk of malnutrition and poor health related to diet. Future concerns should be towards understanding their nutrient intake and improving it.
- Workshop
Session Introduction
Osama O. Ibrahim
Bio Innovation,USA
Title: Sweeteners in our diets and world health organization guidelines on free sugars intake

Biography:
Osama Ibrahim is a highly experienced, principal research scientist with particular expertise in the field of microbiology, molecular biology, food safety, and bio-processing for both pharmaceutical and food ingredients. He is knowledgeable in microbial screening /culture improvement; molecular biology and fermentation research for antibiotics, enzymes, therapeutic proteins, organic acids and food flavors, biochemistry for metabolic pathways and enzymes kinetics, enzymes immobilization, bio-conversion, and analytical biochemistry. He was external research liaison for Kraft Foods with Universities for research projects related to molecular biology and microbial screening and holds three bioprocessing patents. In January 2005, he accepted an early retirement offer from Kraft Foods and in the same year he formed his own biotechnology company providing technical and marketing consultation for new start up biotechnology and food companies
Abstract:
World Health Organization (WHO) refers to monosaccharides of glucose, fructose, and disaccharides of sucrose, maltose that added to foods, drinks, baked goods and confectioneries, plus sugars presents in honey, fruit juice and fruit juice concentrates as a free sugars or added sugars because there is strong evidence of high risk of overweight, obesity and tooth decay from consuming of these type of sugars. WHO does not refer to naturally sugars present in fresh fruits, vegetables and milk as free sugars but refer to them as natural sugars or intrinsic sugars because they are encapsulated by plants cell wall or naturally occurred in milk and are digested slowly to inter blood stream comparing to free sugars and there is no reported evidence of adverse effects from the consumption of these naturally present sugars in fruits, vegetables, grains, milk or milk products
WHO study group in 1984 recommended the daily consumption (intake) of free sugars should be less than 10% of total daily energy source to reduce the risk overweight, obesity and tooth decay. This 1984 WHO guideline was further elaborated in 2002 by a joint WHO/ FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) expert consultation. The new updated WHO guideline is calling for further reduction (if possible) the consumption of these free sugars to less than 5% of total energy source to halt the rise of diabetes, obesity and to reduce the burden of premature death due to communicable diseases (NDCs)
Sugars metabolic pathways and WHO regulations of free sugars intake will be highlighted in this presentation
- Clinical Nutrition|Diet and Nutrition|Nutrition through Life courses|Diet and Appetite
Session Introduction
Vera Matta
Sweet Diet Clinic,Lebanon
Title: Factors associated with obesity among adolescent girls from lebanon

Biography:
Vera Matta is a Clinical dietitian with more than 7 years of practice,consultant for many food companies, researcher in health ,lecturer in different congresses worldwide, owner of sweet diet clinic Lebanon. She earned her master and PhD degree in nutrition psychotherapy and currently completing her second PhD in clinical nutrition
Abstract:
Background:
Obesity is an emerging public health problem in lebanon and in the whole world too. It is considered one of the death factors worldwide. Alarming rates of overweight and obesity have been rising progressively in Lebanon especially among adolescents.
Aims:
To determine the dietary and lifestyle factors associated with general obesity among adolescents, a cross sectional survey was conducted including a representative sample of 300 lebanese adolescent girls .
Methods:
Data were collected using a standardised questionnaire to determine sociodemograpgic characteristics, dietary patterns and physical inactivity. Body mass index (BMI) was evaluated using the center of disease control BMI for age percentiles.
Multiple logistic regression analysis revealed that skipping breakfast and physical inactivity were the most significant reason for the rising obesity among this age group. Several awareness steps should be taken in order to limit rates of obesity.
- Clinical Nutrition,Optimization Techniques in Nutrition,Food Informatics,Regulations and Packaging,Diet and Appetite,Food Engineering

Chair
Osama Ibrahim
Bioinnovations,USA
Session Introduction
Ozlem Tokusoglu
Celal Bayar University,Turkey
Title: Food Safety Appropriate and HMF Decreased Special Spice Blend Paste

Biography:
TokuÅŸoÄŸlu has completed her PhD at Ege University Engineering Faculty, Dept of Food Engineering at 2001. She is currently working as Associate Professor Dr faculty member in Celal Bayar University Engineering Faculty Department of Food Engineering. TokuÅŸoÄŸlu performed a visiting scholar at the Food Science and Nutrition Department /University of Florida, Gainesville-Florida-USA during 1999-2000 and as visiting professor at the School of Food Science, Washington State University, Pullman, Washington,USA during April-May 2010. She has published many papers in peer reviewed journals and serving as an editorial board member of selected journals. TokuÅŸoÄŸlu published the scientific edited three International book entitled Fruit and Cereal Bioactives: Chemistry, Sources and Applications and entitled Improved Food Quality with Novel Food Processing by CRC Press, Taylor & Francis,USA Publisher, third book Food By-Product Based Functional Food Powders ; Dr Tokusoglu also published three national books entitled Frying Oil Science and Tehnology; Cacao and Chocolate Science and Technology and Special Fruit Olive: Chemistry, Quality and Technology. She organized and/or administered as Conference Chair at many conferences and congress in various parts of USA and Europe. She is Nutrition and food Technology Group Chair of ConferenceSeries LLC, USA
Abstract:
Currently, the potential utilization of the bioactive phenolic major components has been the focus of attention due to their consumption imparts health benefits containing several types of cancer, reduced risk of coronary heart problems. Dietary supplements, food tablets and/or food fortification based on food by-product may be alternative for above-mentioned healthy constituents.
Mesir paste, also known as ‘mesir maccun,’ is a traditional confectionery product with spesific flavor, taste, aroma, taste, colour and high viscosity. Mesir paste contains 41 types of spices and medical plants including different plant extracts with sugar and the health beneficial effects have been reported for hundreds based on some documents thousands of years owing to their bioactive effective phenolic compounds. But in mesir preparation, blend of spices and medicinal plants have been boiled with sugar at high temperature. Nowadays, it is known that 5-hydroxy methyl furfural (HMF) formed during thermal decommission of sugars and carbohydrates and it is an aldehyde and a furan compound [namely as is 5-(hydroxyl methyl)2-furan carboxaldehyde], this formation provide an indication of overheating and storage in poor conditions. Even though, HMF is not yet considered a harmful substance, the National Institute of Environmental Heath Science nominated HMF for testing based on the widespread of HMF in daily consumed foods, evidence for carcinogenic potential of other members of this class and the fact that little is known about HMF toxicity. It is known that the reported toxicity tests are mostly confined to mice and rats.
In this research workshop content, we found that several factors (such as temperature, duration of heating process, storage conditions, pH and floral source) influence HMF levels of mesir paste. By using our developed manufacturing metholody, HMF levels was decreased to 2.12-8.71 mg/kg (ppm) from 158-196 mg/kg (ppm) by depending on Ottoman traditional manufacturing. Insomuch that, 30.55; 68.09; and 88.75 ppm
results were achieved by 15.day, one month and 2 months of storage, respectively (p<0.05). Based on Turkish Food Codex Sugar, Confectionery Products & Honey Communique, max.level of HMF must be 40 ppm in final products so it is seen that great data was obtained and it was determined the storage stability for production shelf life. An analytical good correlation was found with good performance in terms of precision for the method (p<0.05). In mesir paste, subsequent to fundamental chemical analysis (sugar, invert sugar, total carbonhydrate, total protein, total fat, total ash and total fiber); the avg.486 mg gallic asid equivalent phenolics [mg gallic asid equivalent (GAE) phenolic /100g], the total flavonoid concentrations were avg.786 mg quercetin equivalents (QE) /100 g paste whereas the IC50 of the methanolic extracts was avg.1.196 mg paste/ml and the results showed that sinapic acid was most active in the DPPH (IC50 value 0.0176 ± 0.002 mg paste/ml). Majorly cinnamaldehyde, shringic acid, sinapic acid, vanillic, ferulic, cafeic, chlorogenic acids, 4-caffeoylquinic, 1,3- caffeoylquinic acid, 1,4-caffeoylquinic, 1,5-caffeoylquinic acids, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, p-coumaric acid, protocatechuic acid, coumarin, piperine, sinapin, a-Zingiberene 10-Gingerol, curcumin, cubebin, kampferol, quercetin, 3¢-O-metyl quercetin, acacetin phenolics, lignan glucoside trachelosid lignin were identified by both HPLC-DAD and LC-ESI-QTOFF-Mass Spectrometry as qualitative and quantitavely. Also piperolein, beta-bisabolen, öjenol, methyl öjenol, öjenol asetate, mirisen, beta-karyofilen, alfa-pinen, linalool, alfa-pinen, campfore, alfa-cububen, alfa-kopaen, trans-anethol, estragol, anise ketone, anisic acid, geranial, geraniol, 6-shogaol, zingeron, miquelian were determined as volatile components by GC-MS.
Scientific evidence shows that some dietary supplements are beneficial for overall health and for managing some health conditions. By utilizing of 41 spices and medicinal plants, mesir tablet was produced at DEPARK Technopark Spil Innova LLCas industrial health innovative. We discussed chemical characterization, functional properties, their unique bioactive features of mesir effervecent tablet and covered antioxidative, anticarcinogenic reports.
Ron Judge
Maple Lodge Farms,Canada
Title: Meeting Expectations: Ritual Dietary Laws into a HACCP approach

Biography:
Ron Judge has worked in the food industry his entire career in the area of food safety and quality assurance both in corporate positions and as a consultant. He has consulted for over 25 different companies across North America ranging from chocolate, pastries to slaughter and ready to eat meat products. His corporate positions include working for Campbell Soup Company, Maple Leaf Foods and most recently with Maple Lodge Farms as their Director – Food Safety, Quality Assurance and Animal Welfare. Ron’s mandate at Maple Lodge is to elevate all of their food safety, quality assurance, and animal welfare programs to a higher level of standard as Canada’s largest poultry slaughter company looks for future expansion of its halal products and customer base.
Abstract:
Global expectations within the food industry is that companies will increasingly to take more initiative in terms of halal quality and food safety to protect their brands. Since 1990, Maple Lodge Farms has been recognized the demand for food compliant with Islamic dietary law (halal), with primary consumer choices based on quality and safety. The Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) -based halal quality-assurance standards were developed as a result, using the HACCP criteria for safety (recognized by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency), religious dietary requirement and quality. Halal critical control points (HlCCP) are identified using HACCP criteria and a question tree on HALAL processing and storage. This approach harmonizes and unifies halal processing with the specific food industry via an HACCP–based halal quality-assurance system. Principles of this program include the following: 1) the traditional method of slaughtering in Islam is to slit the throat, cutting the carotid arteries, jugular veins, trachea, and the esophagus, without severing the head.
2) It must be done by a Muslim of sound mind and health while pronouncing the name of God on each animal or bird. 3) Muslim slaughter persons is required at each line. The number
of slaughter persons depends on line speed, size of the animals, and number of hours the operation will be performed. 4)
Maple Lodge uses the machine slaughter of birds, which is very precise. Thus method is approved by our Muslim certification body. Almost all countries that import chicken are now accepting machine-killed birds. Our plants are federally inspected, HACCP and BRC certified (two of the most rigorous standards for food safety).
Halal Controls Points in Poultry Slaughter


Biography:
To be updated
Abstract:
Introduction
Pancreatic enzyme preperations are a life-saving substitution for a pivotal physiological function of the entire organism that is impaired in chronic pancreatitis with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Pancreatic enzyme preperations, generically called pancreatin, are not alike. Rather, they present a broad variety of pancreatin composition. Our aim with this study is to compare efficacy of enteric-coated mini-microsphere pancreatin product in respect with regular pancreatin products as the clinical outcome and symptomatic improvement of patient and beneficial effect especially on nutritional status in patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
Patients and Methods
A total of 53 consecutive patients (34 male, 19 female) with exocrine pancreatic defficiency due to chronic pancreatitis were included the study. 24 patients were treated with regular pancreatin products(Group1), 29 patients were treated with enteric-coated minimicrosphere pancreatin product (Group 2) . Symptoms, quality of life, nutritional status, pancreatic function were assessed before and after treatment. Quality of life was assessed with The Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT) Measurement System as a collection of health-related quality of life (HRQOL) questionnaires targeted to the management of chronic illness.
Results: Steatorrhea incidence was significantly lower in Group 2 compaared with Group1 (p<0.05). Abdominal pain score was significantly lower in Group 2 compared with Group1 (p<0.05). Median FACIT score of Group 2 was significantly higher than Group 1 (p<0.05). Median BMI was significantly increased in Group 2 in respect to Group 1 (p<0.05).
Discussion: Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is a serious condition which occurs in several diseases including chronic pancreatitis , cystic fibrosis, pancreatic cancer, and as a result of pancreatic surgery. The lack or absence of pancreatic enzymes leads to an inadequate absorption of fat, proteins, and carbohydrates, causing steatorrhoea and creathorrhea which results in abdominal discomfort, weight loss, and nutritional deficiencies. To avoid malnutrition related morbidity and mortality, it is pivotal to commence pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy as soon as exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is diagnosed. Factors as early acidic inactivation of ingested enzymes, under dosage, and patient incompliance may prevent normalisation of nutrient absorption, in particular of fat digestion.
The most important aspect of the major therapy seems to be bioavailability of the product to enhance optimal absorbtion of food and especially fat. Enteric-coated mini-microsphere pancreatin product is shown more efffective in this study
Subhajit Ray
Central Institute of Technology, India
Title: Formulation of carrot powder fortified value added biscuit for nutritional and health benefits

Biography:
Subhajit Ray has completed his PhD degree from Jadavpur University in India. He has more than 20 years of experiences including 21 years of teaching and one year of industrial experiences. Currently he is an Associate Professor, Department of Food Engineering and Technology, Central Institute of Technology in India. He has published more than 30 papers in reputed journals, and participated and presented in numerous national and international conferences. He has been serving as a Member of Reviewer Panel and an Editorial Board Member in many reputed national and international journals.
Abstract:
In recent years, the consumption of carrot and carrot powder as well has increased steadily due to the recognition of ant oxidative and anticancer activities of β-carotene. The aim of this research project was to develop carrot powder fortified value added biscuits. First of all carrot purchased from local market of Kolkata was blanched in cube form, dried and finally grinded to powder form. Prepared carrot powder was evaluated for physicochemical properties viz. sensory and chemical qualities. In the present study the moisture,ash,fat,carbohydrate and protein of raw carrot were estimated as 91.25%,.39%,.59%,3.84% and 3.93% respectively. The nutritional quality parameters viz. ascorbic acid, moisture, fat, ash, carbohydrate and protein content of carrot powder were analyzed as 2.6×10-4 mole/l, 16.5%, 2.24%, 1.48%, 3.52 g and 7.71%, respectively. Now carrot powder fortified biscuits were formulated by incorporating 5%, 7.5% and 10% carrot powder with ordinary flour. The experimental result revealed that carbohydrate content of 10% carrot powder fortified biscuit and protein content of 5% carrot powder fortified biscuits were enhanced as 72% and 64.49%, respectively. The β-carotene content in the different carrot powder formulated biscuits viz. 5%, 7.5% and 10% were also estimated as 0.092 mg/gm, 0.192 mg/gm and 0.187 mg/gm, respectively. So 7.5% carrot powder fortified flour blend was found to be maximum β-carotene content and overall acceptability score, respectively. Therefore in this study 7.5% carrot powder flour blend for biscuit preparation was found to be optimum in terms of nutritional quality, sensory acceptable in context to nutritional importance.

Biography:
Souheir Alia has her expertise in health education and promotion in both community setting as well as hospital setting, and works as a Clinical Dietitian in Rashid Hospital, DHA, in the city of Dubai, in UAE.
Abstract:
Obesity is considered to be a disease, which stands alone by itself and it is accompanied by many comorbidity and that is why many means to treat obesity comes into account and one of the most prevalent ways in UAE is by bariatric surgery. Despite the vast research assessing nutrition knowledge of patients of several health conditions, none of the papers assessed the nutrition knowledge of patients’ post-bariatric surgeries, although this category of patients is very susceptible to malnutrition post-surgery. My aim in this study was to assess the general nutrition knowledge and the knowledge specific to the dietary protocol post-surgery, the medical and nutritional complications and their awareness and understanding of dumping syndrome specifically, the clarity of information conveyed by the dietitians and its effect on their levels of compliance of the post-bariatric surgery dietary protocol and the follow up appointments with the dietitians and finally a small part gave a glimpse of their quality of life post-surgery.
The method used to analyze the questionnaire was with the help of SPSS version 23.0. Descriptive statistics such as frequencies, proportions, means and standard deviations were used. Statistical tests such as Chi-Square test of independence and Pearson’s correlation were used to test correlation. To test significant differences between values of quantitative variable were used using the statistical test ANOVA or its equivalent non-parametric test named Kruskal-Wallis. Normality was tested using the Shapiro-Wilk test, while Levene’s test was used to test the equality of variance. The results of this study showed fairly good general nutrition knowledge of both groups, the questions assessing nutrition knowledge of the dietary protocol post-surgery were added up and given a score out of 14, in which it showed that only 19.4% of participants had very good knowledge, 66.2% had average knowledge, and 14.4% had poor knowledge. In addition, most patients didn’t know what dumping syndrome is and of those who knew what it is 66.6% of them knew the food that promote its occurrence and almost half of the participants who answered yes knew the symptoms of it. On the other hand, 79.5% of the patients followed up with a dietitian and only 30.1% showed compliance to the dietitian’s instructions, which was strongly related to patients finding the information conveyed vague and unclear as 71.2% considered it as aforementioned. However, the most experienced symptom post-bariatric surgeries were nausea, followed by dizziness, dehydration and finally vomiting. As for the overall quality of life of participants the highest percentage 45.8% was given to participants who never felt agitated, fatigued and/or regretted their decision of getting operated and as much as 83.1% found their daily activities to be more enjoyable. In conclusion, patients who undergo bariatric surgeries are a great area of improvement now that we can spot some gaps in the health care provided.

Biography:
Harini N B has completed her MSc and BSc Degrees in Clinical Nutrition from Sri Ramachandra University and Ethiraj College for Women, respectively. She is currently a Consultant Nutritionist at Almond board of California and delivers lectures on the importance of the nutritional values of almonds and its health benefits. She worked at the Apollo hospitals, India as a Clinical Dietitian Associate for a year where she performed nutrition counseling assessed the nutritional requirements and developed nutrition counseling programs for the patients and suggested diet charts to meet individual’s requirements. She was actively involved in organizing the Bariatric nutrition conference “Enlight 2016”.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Oncology patients undergoing chemotherapy normally tend to have gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea and vomiting. Good nutrition counseling associated with strategies to reduce nausea and vomiting can help to reduce the intensity of such symptoms and help the patients to have a better quality of life.
Aim: To evaluate the effect of ginger extract in reducing chemotherapy induced nausea, vomiting and improve nutritional status, quality of life of oncology subjects on chemotherapy.
Objectives: To evaluate nutritional status, appetite and weight loss, quality of life of subjects on chemotherapy and to supplement ginger extract and evaluate effect on selected parameters.
Materials & Methods: A prospective experimental study was carried out on 80 subjects (40 F, 40 M) on 1st cycle chemotherapy. Subjects consumed 50 ml of ginger extract containing 1.5 g ginger for a period of four days till the third cycle of chemotherapy. Baseline assessment was done using PG-SGA, FACT-G and SNAQ questionnaire measuring nutritional status, quality of life and weight loss, respectively. Days of chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) was measured using MASCC tool.
Results: Significant (p<0.001) improvement in nutritional status (PGSGA) scores, quality of life (FACT-G) scores and prediction of weight loss scores (SNAQ) was observed between baseline and final assessments. Number of days of CINV reduced significantly (p<0.001) from 5.74±2.19 to 3.92±1.10.
Conclusion: Few studies have reported the use of herbal anti-emetics in reducing CINV, equivalent to allopathic anti-emetics. Present study also has shown the use of Zingiber officinale to be effective in reducing the number of days of chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting.
Huda Mohammed Albarnawi
Heriot-Watt University, UK
Title: Isolation and characterization of protein from date palm fruit (Phoenix dactylifera L.)

Biography:
Huda Mohammed Albarnawi is a Teaching Assistant at Um Alqura University in Saudi Arabia in Makkah. She has completed her MSc in 2014 from Heriot Watt University. Currently she is pursuing her PhD from the same university
Abstract:
This study investigated the antioxidant, functional properties, and proximate analysis of date fruits protein isolate (DFPI) using standard analytical methods. In this study, the author extracts and determines the protein from date palm fruit (Shalaby) at the Tamar stages of maturity by three methods. The most efficient method resulted in a protein concentrate containing 5.42% of the protein of which the soluble fraction was 3.05% and insoluble protein was 2.37%. The protein extraction method improved to a level of 20% protein in solution as determined by the Kjeldahl method. The results detected that the antioxidant activity using the ferric reducing antioxidant potential assay (FRAP) showed a higher value for date fruit than ascorbic acid at 20 mg/ml versus 7.60 mmol/g. Proteomics analysis by Liquid-chromatography coupled mass spectrometry (LC−MSMS) showed that the major fractions were metabolism proteins (21%), protein related to energy (16%) and storage proteins 13%. Determination of the effect of pH and temperature on protein solubility of date and soy protein showed that both types of proteins were more soluble at pH 6 and 7. Maximum solubility at this pH range for DFPI was at 55 oC, compared to 65 oC for soy protein isolate (SPI). The functional properties determined (the emulsifying and foaming ability) of DFPI compared to that of SPI. The physicochemical properties measured electrophoretic pattern, turbidity, sulfhydryl groups and hydrophobicity of DFPI compared to that of SPI. The effect of heat treatment on the functional properties and physicochemical properties identified DFPI and SPI as a function of SH groups, hydrophobicity and turbidity.

Biography:
To be updated
Abstract:
Introduction
Pancreatic enzyme preperations are a life-saving substitution for a pivotal physiological function of the entire organism that is impaired in chronic pancreatitis with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Pancreatic enzyme preperations, generically called pancreatin, are not alike. Rather, they present a broad variety of pancreatin composition. Our aim with this study is to compare efficacy of enteric-coated mini-microsphere pancreatin product in respect with regular pancreatin products as the clinical outcome and symptomatic improvement of patient and beneficial effect especially on nutritional status in patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency.
Patients and Methods
A total of 53 consecutive patients (34 male, 19 female) with exocrine pancreatic defficiency due to chronic pancreatitis were included the study. 24 patients were treated with regular pancreatin products(Group1), 29 patients were treated with enteric-coated minimicrosphere pancreatin product (Group 2) . Symptoms, quality of life, nutritional status, pancreatic function were assessed before and after treatment. Quality of life was assessed with The Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT) Measurement System as a collection of health-related quality of life (HRQOL) questionnaires targeted to the management of chronic illness.
Results: Steatorrhea incidence was significantly lower in Group 2 compaared with Group1 (p<0.05). Abdominal pain score was significantly lower in Group 2 compared with Group1 (p<0.05). Median FACIT score of Group 2 was significantly higher than Group 1 (p<0.05). Median BMI was significantly increased in Group 2 in respect to Group 1 (p<0.05).
Discussion: Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is a serious condition which occurs in several diseases including chronic pancreatitis , cystic fibrosis, pancreatic cancer, and as a result of pancreatic surgery. The lack or absence of pancreatic enzymes leads to an inadequate absorption of fat, proteins, and carbohydrates, causing steatorrhoea and creathorrhea which results in abdominal discomfort, weight loss, and nutritional deficiencies. To avoid malnutrition related morbidity and mortality, it is pivotal to commence pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy as soon as exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is diagnosed. Factors as early acidic inactivation of ingested enzymes, under dosage, and patient incompliance may prevent normalisation of nutrient absorption, in particular of fat digestion.
The most important aspect of the major therapy seems to be bioavailability of the product to enhance optimal absorbtion of food and especially fat. Enteric-coated mini-microsphere pancreatin product is shown more efffective in this study

